The principle entails extracting a sample of stack gases, passing it through a filter to remove particulate matter, and then passing it through a condenser to collect the condensate produced in the process. The aim of the test is to collect and calculate the volume of all condensate produced from a given amount of gas at the condensing temperature.
Procedure: Water vapour is uniformly distributed in the gas stream except in rare conditions, so sampling for moisture determination does not need to be isokinetic and is not sensitive to duct location. The sampling nozzles should be placed downstream to reduce the pressure drop across the thimble caused by particulate capture. At a rate of about 500 ml/sec, sample the gas. Run the test until you have enough condensate to make an accurate calculation. Measure the temperature and pressure of the condenser close to the metre, since there would be a negligible pressure drop in the line between them. In order to measure the moisture content, the metre pressure may also be substituted for condensate pressure. Measure the volume of condensate collected in a graduated measuring cylinder
Apparatus: Particulate Sampling Apparatus, Condenser, Dry Gas Meter, Gauges, Gas Pump, Fittings
Calculations
Calculate the volume of water vapour collected using the following equation:
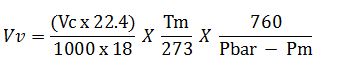
Vv = Equivalent vapour of condensate under sampling condition, m3
Vc = Volume of condensate in condensor, ml
Tm = Temperature at metering condition, °K
Pm = Suction at meter, mm mercury column
Pbar = Barometer pressure, mm mercury column
Calculate the moisture content of the gases using the following equation:
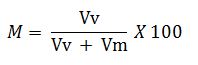
Where
M = Moisture in the flue gases, percent
Vv = Equivalent vapour volume of condensate under sampling condition.
Vm = Volume of gas sampled (m3)

















